
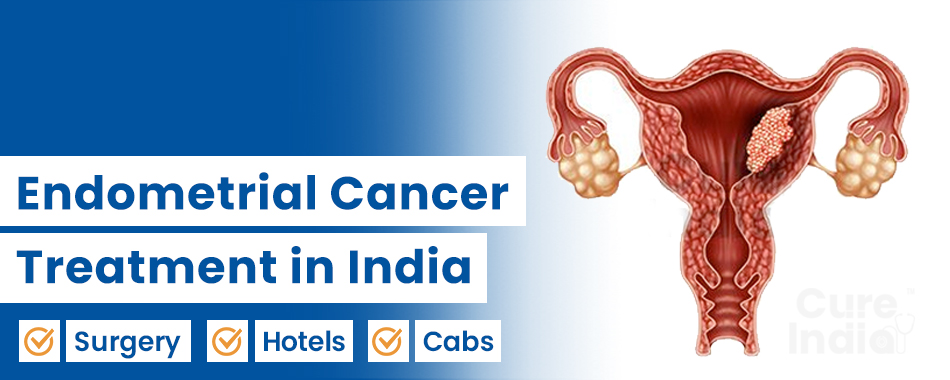
Endometrial cancer is also known as uterine cancer. The cancer occurs in the innermost lining of the uterus. In addition, the uterus is a pear-shaped organ. It is hollow and lies inside the pelvic region. It is a part of the female reproductive organ where the fetus grows and nourishes.
The uterus has two parts. The upper part is the uterine cavity and the bottom part is the cervix. The cervix then continues into the vagina. The uterine cavity is where the endometrium layer forms a glandular, thick tissue layer rich in blood vessels to conceive the baby.
When the pregnancy does not occur, the endometrium layer then sheds. This phenomenon is what we call menstruation. When the cells of the endometrium layer inside the uterus develop the change (mutation) in its DNA (genetic material), they become cancerous. These cells start multiplying rapidly and form a tumor.
Endometrial or uterine cancer is one of the most common cancers that females develop. Endometrial cancer is one of the fatal diseases among women in African countries. With the rise in cancer cases in Africa, a lot of people are unable to receive the proper diagnosis and early treatment due to a lack of cancer awareness, inadequate diagnostic and screening facilities, and a shortage of specialized oncologists and medical staff. In addition to this, the cost of vaccination and treatment is high with the low capacity of the hospitals to take the patients.
Studies show that by the year 2030, there will be a 70% rise in cancer cases due to:
All the above reasons lead to high mortality rates and morbidity rates. The low and middle-income countries are slow growing in the healthcare sector. That is why, a lot of women from African countries like Kenya, Ghana, Tanzania, and Rwanda visit India every year for the correct diagnosis and treatment of uterine cancer.
Indian cancer hospitals have the most up-to-date treatment protocols and diagnostic tools for high-quality treatment at very cost-effective rates. India is the most affordable country to receive endometrial cancer treatment.
The endometrial cancer hospitals in India have the most innovative and modern technologies for early diagnosis and treatments with high success rates. The oncologists in Indian cancer hospitals are experienced in handling complex cancer cases. They have been in medical practice for many years and acquired ample knowledge.
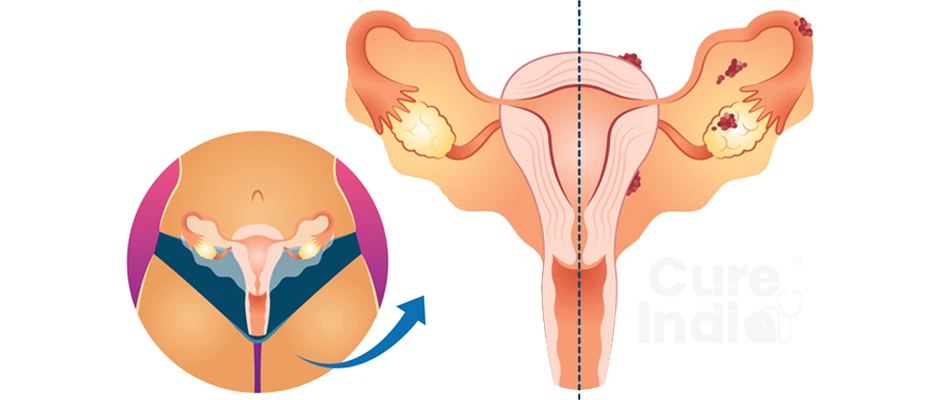
Endometrial cancer commonly known as uterine cancer is one of the common cancers that occurs in females. The uterine cancer begins when the DNA change (mutation) occurs in the healthy cell which makes the cells grow and multiply rapidly.
As these cells grow, they form a mass of cells known as a tumor. Now, this tumor can be cancerous or non-cancerous. If the tumor is non-cancerous, then it does not spread elsewhere in the body. It does not cause major health problems in the body. On the other hand, if the tumor is cancerous, it can spread to nearby organs and tissues to distant organs in the body through the bloodstream or the lymph nodes.

Following are the cancerous and non-cancerous conditions that can arise in the uterus. The non-cancerous conditions in the uterus include:
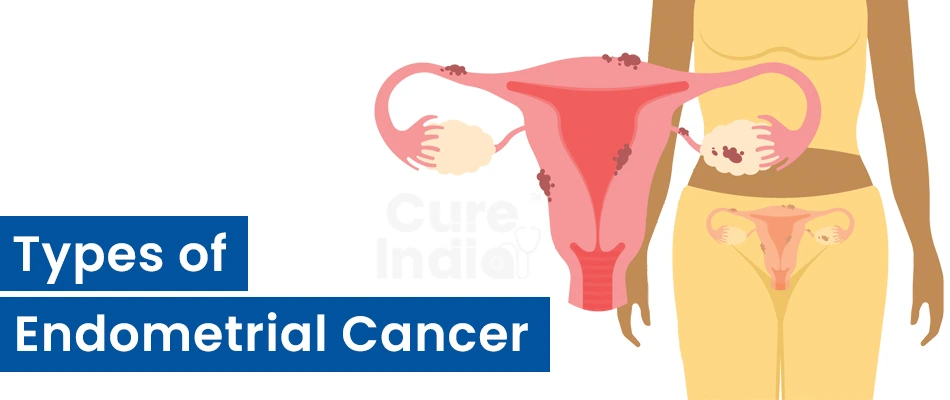
When we talk about the types of cancer that can occur in the endometrial lining or the uterus, they are majorly of two types. There are different stages of these cancers depending upon how severe they are and whether they have spread to the surrounding tissues of any organs of the body. The two major types of uterine cancer along with their subtypes are listed below.
This is the uterine cancer that the majority of females develop. About 80% of uterine cancer is adenocarcinoma. It starts from the cells that line the uterus, commonly known as endometrium. It is also known as a type 1 uterine cancer. There are a few subtypes of this category which are mentioned below.
This is a type of uterine cancer that starts from the supporting tissues of the uterus which is known as a myometrium. The myometrium is the muscle of the uterus. This is a rare type of uterine cancer, about 2 to 4 percent of people develop this type of cancer. It is also known as type 2 uterine cancer. There are a few subtypes of this category also, which are mentioned below.
The exact cause of endometrial cancer is still unknown. However, due to a genetic mutation of the cells in the endometrium, the abnormal cell growth begins. These abnormal cells grow and multiply at a very fast rate. These cells also kill the healthy cells. When these abnormal cells accumulate, they form a thick mass of cells which is called a tumor. These cancer cells may or may not spread in the nearby tissues and organs. They can even spread to other distant organs in the body which is called metastasis (spread of cancer). Some risk factors that increase the chance of developing uterine cancer, are:
You must consult your gynecologist if you have any of the endometrial cancer symptoms mentioned above. The specialists who diagnose and treat the cancers of the female reproductive organs are known as gynecologic oncologists. They will then recommend the tests to examine the signs of the possible diseases. These diagnostic tests help diagnose the presence of the cancer, its current stage, type, and spread extent. They guide specialists to choose the best treatment procedure for you. Following are the diagnostic tests that your doctor recommends.
Medical history is important as it plays a major role in determining the cause of the medical condition you have. Your doctor may also ask you about your family history. If someone in your close family has a history of cancer or uterine cancer, then there are chances that you will also develop the cancer. Your doctor will also ask about your overall health, any present medical conditions, etc.
The pelvic exam is done to see any signs of lumps or other abnormalities in the pelvic area and the organs lie in the pelvic area. Your doctor may inspect your reproductive organs such as the vagina, vulva, cervix, uterus, etc. The doctor may examine the vagina of a patient to feel any abnormalities present there.
The blood test is an important test that helps your doctor to know whether you have an infection in the body. If there is any infection in the body, then the blood test will show it. If a woman has cancer of the uterine lining, then the blood will contain increased levels of some significant compound.
This is a test in which the cervical tissue sample is collected for laboratory testing. The Pap test helps to find the cancer cells and the cells in their pre-cancerous stage. The doctor may suggest some limitations for about 48 hours before the Pap test.
A small tissue sample is taken from the uterus with the help of a suction that is applied through a thin tube. This tissue sample. Then, the sample is sent to the laboratory for testing. A specialist known as a pathologist will examine this tissue under a microscope and check for the presence of any abnormal cells.
This is a procedure that is similar to the biopsy. In this procedure, the patient is given anesthesia for a painless procedure. The doctor inserts the thin flexible tube in the uterus through the vagina and cervix. Then, the doctor collects the tissue from the uterus and sends it to a lab for testing.
Imaging tests like transvaginal ultrasound use sound waves to create images of the uterus for checking the condition of the uterus. Another imaging technique is a CT Scan which uses X-rays to take pictures of the organ under examination from different angles. Your doctor will see this image to check for any abnormalities present in the uterus. An imaging test known as an MRI Scan uses the magnetic field to create images from different angles and merge the images to create a detailed image. Some of the similar tests known as PET scans are also used in the same manner.
This test is generally used to determine whether the tumor is cancerous or non-cancerous. Biomarkers are the molecules that are specific to the cells the doctor examines. In case of cancer cells biomarkers such as proteins, specific genes, and other factors are checked for. These materials are unique in the cancer cells and are not present in the normal and healthy cells. So we can easily differentiate between cancer cells and healthy cells.
The hysteroscope has an attached camera and lighting device that helps in visualizing the inside cavity of the uterus. This procedure helps collect a sample of the uterine lining to send it to the lab for further testing.
CureIndia helps you connect with the top doctors for your endometrial cancer treatment in India. The oncologists at CureIndia are highly experienced in diagnosing and treating endometrial cancer, providing personalised treatment plans that can include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, depending on the needs of the patient. CureIndia provides comprehensive treatment services that include detailed consultations, advanced treatment options, and ongoing support throughout treatment. Let's hear from some of our leading doctors for endometrial cancer treatment in India:
Dr. Rama Joshi is a highly experienced gynecologic oncologist with around 30 years of experience in managing endometrial and other uterine cancers. She specialises in advanced surgical techniques, including chemotherapy and surgery options, ensuring comprehensive gynecological treatment for her patients.

Dr. Sabhyata Gupta is an experienced gynecologic oncology specialist in India with over 23 years of expertise in treating endometrial cancer and other complex gynecologic malignancies. She is known for her evidence-based treatment strategies, meticulous surgical skills, and successful treatment outcomes.

Dr. Rupinder Sekhon is a distinguished gynecologic oncologist with around 16 years of experience in managing endometrial, cervical, and ovarian cancers. She specialises in advanced surgical oncology, chemotherapy, and multidisciplinary cancer care, providing patients with prsonalised treatment plans.

Dr. Surender Kumar Dabas is a top-rated surgical oncologist with over 20 years of experience in diagnosing and treating cancers, including endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer and more. Known for his expertise in minimally invasive and robotically assisted surgeries, he delivers personalised treatment plans that prioritise patient safety and optimal outcomes.

The total cost of endometrial uterine cancer treatment in India is influenced by many factors such as the chosen hospital and its infrastructure, selected treatment approach, diagnostic tests performed, medications, location of the hospital, surgeon’s fees, travel and stay cost, etc. However, on average, the endometrial or uterine treatment cost in India can range between $4,500 to $6,000. The cost of endometrial cancer treatment in the USA, UK, and Australia can range between $5,000 to $15,000, $16,500 to $25,500, and $13,300 to $33,200 respectively.
For a better understanding, the costs of different treatments for endometrial cancer are listed below.
| Treatment Name | Cost in India | Stay in India |
|---|---|---|
| Endometrial Cancer Treatment in India | $1,000 - $7,000 | 3 Weeks |
The cost of the complete treatment including the follow-up sessions is much lower in India as compared to many other countries. India has the most experienced gynecologic oncologists who provide the best possible treatment considering the patient’s health condition, stage and type of cancer, and minimum invasion. With the affordability of the treatments, the quality of the medical care remains supreme with modern infrastructure and facilities and highly cooperative medical staff.
A multidisciplinary medical team provides the treatment of uterine cancer. It means a group of doctors work together to provide the treatment. The doctor who treats the cancer is known as an oncologist, and the doctor who treats the cancer of the reproductive organs is known as a gynecologic oncologist.

The type of treatment that is selected for your treatment depends on many factors like the stage and type of uterine cancer, the patient’s overall health, age, personal preferences, etc. Many times, cancer is treated with a combination of treatments for example, a lot of time chemotherapy is combined with radiotherapy or surgery. This is done to provide effective treatment if the cancer has spread and started affecting other tissues. The different types of treatments for uterine cancer are as follows:
Surgery is done when the cancer is localised. That means, it is present in one organ only and has not spread anywhere else in the body. The surgery is done to remove the tumor from the affected organ. Along with the tumor, some of the surrounding tissue is also removed which is called a margin to prevent the recurrence of the cancer from this site. There are different types of surgery depending upon how much portion is to be removed. The common surgical procedures that are used for removing the tumor from the uterus are as follows:
- Hysterectomy:
This is a procedure that involves removing the uterus (reproductive organs). The hysterectomy is of two major types depending upon the organ removed from the uterus. A simple hysterectomy involves the removal of the cervix along with the uterus whereas a radical hysterectomy involves the removal of the cervix, the upper portion of the vagina, and the nearby tissues along with the uterus. Sometimes the fallopian tubes and the ovaries are also removed along with the uterus. It is known as salpingo-oophorectomy hysterectomy.
- Lymphadenectomy:
This surgery is performed to remove the lymph nodes present near the tumors. This is to make sure that cancer does not spread through the lymph nodes to the other parts of the body. Sometimes, a similar procedure known as a lymph node biopsy is performed in which a dye is injected into the uterus which gets collected in the lymph nodes that contain cancer, these lymph nodes that take up the dye are then removed surgically.
The surgery is performed either laparoscopically /robotically which involves making a few tiny incisions in the abdomen. Laparoscopic surgery is also known as keyhole surgery. The open surgery involves making a large incision in the abdomen.
The doctor who performs this treatment is a specialist known as a radiation oncologist. This method of treatment involves using a high beam (high energy) of radiation (X-rays) and focusing it directly on the cancerous tissue to destroy and kill the cancer cells. This can be done internally or externally. The radiation therapy delivered internally is known as brachytherapy. It is performed by placing the applicators inside the uterus through the vagina and cervix. The radiation delivered externally is known as external-beam radiation therapy. It is performed by using the radiation machine outside the body and focusing the radiation on the pelvic area.
Sometimes the treatment is done through medication which can be given to the patient either orally, intravenously, or intramuscularly. There are many different types of drug therapies which are sometimes combined, and sometimes they are often used with other treatments like surgery and radiation therapy. The drug therapies such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy target the cancer cells and destroy them whereas the drug therapies like hormone therapy and immunotherapy work in different ways. The different types of drug therapy for uterine cancer are listed below.
It is crucial to get regular checkups and screening in order to keep track of the health and any signs of recurrent cancer. Almost all cancer has a chance of recurring. However, if you maintain a healthy lifestyle and follow the guidelines provided by your doctor, you can minimize the cancer recurrence chances.
The cancer is most likely to reoccur within the first 2 years. Hence, must attend follow-up visits after the treatment ends. Your doctor will suggest follow-up appointments for the screening of cancer. For the first 2 years, you will be given appointments every 3 to 6 months and after that, you will be given appointments every 6 to 12 months.
During these appointments, physical exams, CT Scans, Pap tests, and X-rays are done to make sure you are cured. It is also important to take care of yourself by maintaining healthy lifestyle choices like regular exercise, a balanced diet, proper rest and sleep, and maintaining a healthy weight. Along with these, try to avoid alcohol and tobacco products as much as possible.
Endometrial cancer is a condition that many women are suffering from due to the modernized lifestyle in most countries. The diagnosis and treatment procedures are easily available in high-income countries. However, low and middle-income countries lack proper diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for uterine cancer.
In addition to this, there is a shortage of medical experts who provide the correct diagnosis and treatment. It is very difficult for the patient to be mentally and emotionally strong once they are diagnosed with the advanced stage of cancer. Hence, an early diagnosis must be made so the treatment is possible and also when the cancer is in its early stage.
Seeking the correct diagnosis and high-quality treatment options at cost-effective prices many women from these countries visit India. It is because India is the only country where they can receive supreme quality treatment at a very affordable cost. In other countries, high-quality treatment can be received, but the cost is too high that they cannot afford it. Due to this, India has become a medical hub and a boon for international patients.
