
Pediatric cardiac surgery is a term used for various treatment procedures that are performed to treat various heart defects in a child either born with heart defects or may develop heart defects after birth. The heart defects in a newborn baby are known as congenital heart defects (CHDs). The CHDs affect the heart structure and the way it functions in a child. Hence, it also affects the blood circulation in a child. Congenital Heart Defects in a child can be mild such as a tiny hole in the heart or it can be severe such as misformed parts of the heart.
Every year there are 500,000 cases of congenital heart defects (CHDs) reported in Africa. The majority of these cases are from sub-Saharan Africa. Some East African countries such as Tanzania, Uganda, and Kenya have initiated CHD services, but the success rate is low. Annually 300,000 children die due to inadequate healthcare access. Also, there is a shortage of certified cardiac surgeons. The healthcare facilities are not efficient in providing proper care. Especially the diagnostic methods. Most of the children don’t get the right treatment due to misinterpretation of the condition. Because of this reason, many people travel to other countries to get access to the right treatment.
In India, the diagnosis of CHD is efficient due to the protocol followed by the healthcare provider of clinically examining the child after birth and because pulse oximetry screening is done before discharge from the hospital helps in the early identification of CHD. Also, advanced medical facilities such as fetal cardiac imaging and proper perioperative care have made it possible to early diagnosis of the condition which helps in initiating the treatment as soon as possible. The cost of pediatric heart surgery is affordable as compared to different countries, which makes international patients choose India for advanced medical care.
The symptoms of CHD may start as soon as the baby is born or it may develop later in life. Some of the CHDs are mild and don’t need a massive treatment whereas, some of the CHD conditions are severe and require surgery. Learning about the CHD symptoms helps you in navigating your child’s heart health. The symptoms include:

The symptoms of congenital heart defects can be observed in a baby or in adults who have CHD. You should seek your child’s pediatrician’s advice as soon as possible if you observe these symptoms in your child. He/she will discuss your child’s condition with proper treatment.
There are various causes of CHD. The child may have CHD because of the changes in chromosomes or the genes, or there are other factors like the environment, the diet of a mother, the condition of a mother, whether the mother is smoking during pregnancy, etc. The factors that might cause CHD are as follows:
■ Heredity: Children who have one of their parents or siblings with a heart defect are more likely to be born with a Congenital Heart Defect.
■ Mutations: There are several mutations in the DNA of the human body cells that can interfere with the formation of a healthy heart.
■ Other birth defects: Children born with other serious birth defects such as Down syndrome and Turner syndrome may also have to go through pediatric heart surgery.
■ Viral Infections: Pregnant women contracting rubella (German Measles) during the first three months of pregnancy possess a higher risk of having a baby born with a heart defect.
■ Medication: Some medications taken by pregnant women that include elements like lithium, accutane or anti-seizure medications also pose a threat to the child's heart formation.
■ Alcohol: Pregnant women indulging hard in alcohol may have their child born with a syndrome like fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) where children may often have their heart.
■ Smoking: Women smoking during the initial weeks of the pregnancy contribute to the incomplete formation of the child's heart, as the heart starts to develop during the 6 initial weeks of pregnancy, hence contributing to the baby taking birth with a heart defect and needing a Pediatric Heart Surgery.
■ Cocaine: Consumption of drugs like cocaine during pregnancy also contributes to a high risk of the child being born with a Congenital Heart Defect.
■ Maternal chronic illnesses: These may include diabetes, phenylketonuria (PKU), and Vitamin B deficiency.
Congenital heart defects can be categorized into three main categories: Heart valve Defects, Heart wall defects, and blood vessel defects. If you observe the symptoms mentioned above, the following are the possible heart defects in the person or a child having those symptoms:
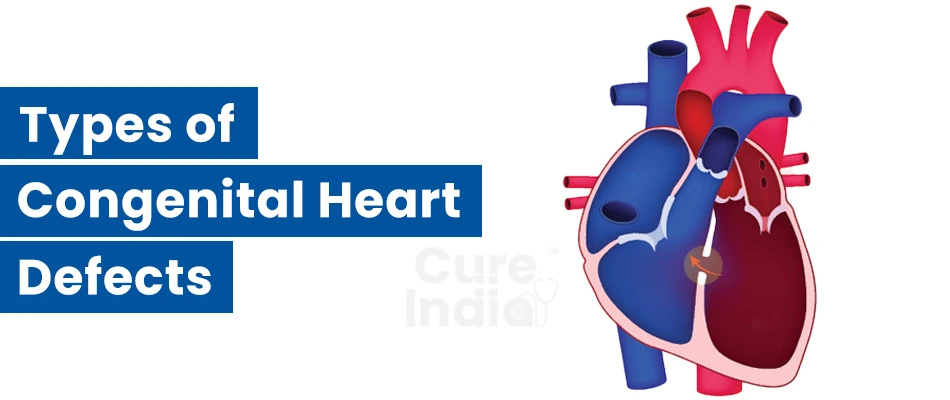
1. Atrial septal defect (ASD): People diagnosed with ASD have a hole between the upper chambers of the heart. The hole increases the blood flowing through the lungs.
2. Atrioventricular Septal defect (AVSD): The other name of this condition is atrioventricular canal defect. In this condition, there is a hole in the walls of the heart chambers. They may also have faulty valves which control the normal blood flow in the heart.
3. Heart Valve Disease: There are four valves of the heart. The function of these valves is to act as a doorway between different chambers of the heart. They are responsible for the proper blood circulation in the body. The valve diseases include valve stenosis and valve regurgitation.
4. Aortic Coarctation: The aorta is an artery. It is the largest artery present in the body and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The constriction in this artery is known as aortic coarctation. Due to this condition, the heart has to pump harder to pump the blood through the aorta.
5. Double-outlet right ventricle: This condition arises when the main arteries i.e., the aorta and the pulmonary artery of the heart do not connect properly to the heart.
6. Ebstein Anomaly: It is a valve disease. The valve involved is the tricuspid valve. This valve is present between the heart’s upper and lower right chambers. The defect in this valve results in poor functioning and the valve does not close properly as a result the blood flows backward i.e., from the ventricle to the atrium.
7. Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA): Ductus Arteriosus is an opening in the blood flow system in a baby in the womb. It closes shortly after the baby is born. Patent Ductus Arteriosus is a condition that arises when it remains open.
8. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR): This is a condition that arises when the blood vessels that connect the lungs with the heart called the pulmonary vein are not attached to the heart properly. This condition is also known as TAPVC- Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection.
9. Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD): When there is a hole that is formed between the ventricles i.e., lower chambers of the heart, the condition is known as ventricular septal defect.
10. Wolff- Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW): The individuals having this condition have extra signal pathways developed between the upper and lower chambers of the heart.
There are many other possible CHDS. These are Eisenmenger syndrome, Kawasaki disease, Hypoplastic left heart syndrome, Long QT syndrome, Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return, Pulmonary Atresia, Patent foramen ovale, Truncus arteriosus, Tetralogy of Fallot, Tricuspid atresia, Vascular rings, etc.
There are several methods that your doctor uses to make a proper diagnosis and interpretation of the symptoms. The most commonly used methods for diagnosis are:
■ Electrocardiogram (ECG): ECG is used to examine the heartbeats. The irregular heartbeats are a sign that you may have a heart defect.
■ Echocardiogram: This method is used to create a moving image of the heart. It uses the sound waves for this purpose. It is most commonly used during pregnancy and is proven to help find CHDs in a baby before birth.
■ Pulse Oximetry: It is a method of determining the oxygen levels in the blood. Chest X-ray: The X-ray can show whether the heart is malformed or has any defects. It can also examine the lungs to see if there is a fluid/blood buildup in the lungs.
■ Cardiac Catheterization: In cardiac catheterization, the doctor uses a catheter and passes it from the artery in the legs to the heart. And examine the heart, whether the blood is flowing in the chambers of the heart, whether the arteries are narrowed, etc.
■ Genetic Testing: This method is used to determine if the genes are responsible for heart defects.
■ Cardiac MRI: This method is used to visualize the detailed images of the heart. Any damage in the specific areas of the heart can be detected.
There are many types of treatment for heart defects. The doctor will examine your symptoms and a proper diagnosis will be made. Based on the diagnosis, your doctor will guide you about what are the possible pediatric cardiac procedures and what is the best approach to treat the condition. In many cases, the heart defects can be resolved by medications. Some cases require small surgical procedures. However, in case of severe heart defects, the doctor may advise you for surgical procedures. There are many different types of pediatric heart surgeries. Some of them are mentioned below:
The baby has a blood vessel known as ductus arteriosus between the aorta and pulmonary artery. This vessel generally closes shortly when the baby starts to breathe after birth. If it does not close, then it creates a problem. This condition is known as patent ductus arteriosus. In most of the cases, this could be treated with medicine. However, if the medicine doesn’t work, then another procedure is used.
Another method to treat this condition is the catheterization approach. In this procedure, a doctor makes a small incision at the groin and inserts a catheter in the artery where the cut is made and then it is moved towards the heart. Then, another device is passed through the catheter to reach into the child’s ductus arteriosus. The device which was inserted through the catheter blocks the blood flow in the ductus arteriosus artery.
However, if the catheter-based approach does not resolve the problem, infant PDA heart surgery is needed. If the child does not have any other problems during PDA then the surgery is avoided for 6 months after the baby is born. In this procedure, first, the medicine will be given to the baby to make them sleep so that they don’t feel pain during the procedure. Then the surgeon will make a small incision between the ribs to reach the PDA artery. The doctor closes the PDA artery with stitches. The cut is then stitched with sutures.
When the child is born with a hole between the right and left ventricles it is known as Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD). Infants who have VSD may have other problems shortly. Doctors perform VSD repair surgery in infants to avoid any other condition arising. During this surgery, your child is given anesthesia to make him/her sleep so that they don’t feel pain during the procedure. Then, the surgeon makes a small incision on the chest of a child to reach the heart. The doctor closes the hole with the stitches. The incision on the chest is then closed. Within 6 months, the patch where the hole is held together with stitches, is completely covered by the child’s heart tissue.
The pediatric open heart surgery is performed to treat various heart problems in the children. The infant open heart surgery is performed in children below the age of 1 year. During this surgery, the child is first given anesthesia to make the procedure pain-free and comfortable. Then, the surgeon will make a small incision on the chest between the ribs, cut the breastbone, and reach the heart. During this procedure, a heart-lung bypass machine is used which continues the normal pumping of the heart while the heart is temporarily stopped. The doctor will then treat the damage in the heart. The heart defects may be in the heart valve, the heart arteries, or the heart wall. Once the repair has been made, the bypass machine is then stopped and the heart is restarted. The doctor then attaches the breastbone with the wires. The incision on the chest is closed with the stitches. The breastbone of an infant is not as hard as an adult. Hence, the recovery is faster as compared to adult open heart surgery.
Pediatric cardiothoracic surgery is performed for various reasons. It is involved in the treatment of organs in the thoracic cavity. The organs such as lungs, heart, esophagus, etc. Cardiothoracic surgery is a general term used for different types of surgeries done in the thoracic cavity. These surgeries include heart surgeries like heart valve surgery, transcatheter procedures, and other advanced cardiac procedures. Based on the treatment required by the patient, the doctor performs the surgery on the target organ.
There are many types of treatment procedures available for pediatric heart defects. However, in severe cases, or when all the other treatments are not possible, the last option is a heart transplant surgery. In a heart transplant procedure, the diseased or failed heart is replaced by the healthy heart. The healthy heart is received by the donor who might not live or may have died. Before this procedure, the surgeon’s team will run some tests to make sure that the donor’s heart is acceptable to the patient. If not done so, the patient’s immune system may reject the new heart.
First of all, the child is given anesthesia to make him/her unconscious. During the heart transplant surgery, the surgeon cuts the chest and removes the diseased heart. The donor’s heart is then placed inside the cavity and the blood vessels (arteries and veins) are then connected to the new heart. The child is then transferred to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) where the child is kept under observation for a few days. His/her heartbeat, oxygen, etc. will be monitored. The child will be on a ventilator and unconscious so that he/she does not feel pain and the doctor will monitor whether the new heart is working properly or not.
Pediatric heart surgery is a highly specialised surgery focused on correcting congenital and acquired heart defects in infants, children, and adolescents. These delicate procedures require not only advanced surgical expertise but also child-focused care and infrastructure. India is home to many internationally trained pediatric cardiac surgeons who perform complex heart surgeries with high success rates, supported by state-of-the-art hospitals and multidisciplinary teams. Some of the most recommended doctors for pediatric heart surgery in India include:
Dr. K.S. Iyer is a top pediatric heart surgery doctor in India with established expertise in complex congenital heart defect repairs, neonatal cardiac surgery, and minimally invasive pediatric procedures. He has successfully performed thousands of pediatric heart surgeries till date, restoring normal heart function and improving survival rates for children with critical heart conditions.

Dr. Anil Bhan is a leading pediatric cardiac surgeon in India, specialising in congenital heart defect corrections, valve repairs, and pediatric bypass surgeries. He is internationally accredited and has performed more than 15,000 cardiac procedures to-date.
Dr. Aseem R. Srivastava is a top-rated pediatric cardiologist in India, with expertise in diagnosis, interventional procedures, and long-term care of congenital heart disease. His areas of specialisation include treating pediatric cardiac defects, such as atrial septal defect and aortic stenosis, with high success rates.

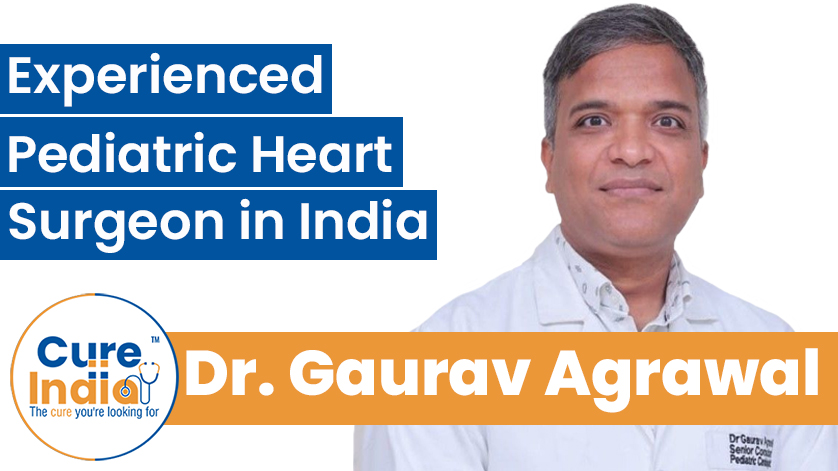
Dr. Gaurav Agrawal is an experienced pediatric heart surgeon in India, with over 17 years of experience in treating complex congenital heart defect repair, performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures, and performing neonatal cardiac surgery. His areas of specialisation include stenting of coarctation of the aorta, pericardial collection drainage, and ASD closure.
The recovery period of different types of treatment for heart repair varies. Some treatment needs only a few days to a week of rest and some of the treatment requires weeks to months of rest. Depending upon the procedure, your child may need to spend a few days in the hospital itself. In case of cardiac surgery, the child is kept under observation post-surgery to ensure that everything is fine and the heart is working properly after the procedure. Once the doctor has confirmation about the proper functioning of the heart, he/she will discharge your child from the hospital with a few guidelines to follow.
The cost of different cardiac surgeries in children varies among different hospitals. The average cost of pediatric cardiac surgery in India is around $6,500 to $7,500. The cost of different types of pediatric cardiac surgeries are mentioned below:
| Treatment Name | Cost in India | Stay in India |
|---|---|---|
| Atrial Septal Defect Repair in India | $6,500 - $7,500 | 10-15 Days |
| Ventricular Septal Defect Repair in India | $7,000 - $7,500 | 10-15 Days |
