Congenital Heart Disease is a heart defect present in the heart due to the abnormalities in the heart's structure from birth. This Congenital Heart Disease affects the blood flow, heart valves and blood vessels. The Congenital Heart Disease can be very serious, given how the heart is responsible for pumping blood to the body and if interrupted, can result in severe complications, leading to death. The Treatments and follow-up care for Congenital Heart Disease have gotten advanced and have been able to save a lot of children's lives who were born with Congenital Heart Disease but were still able to survive into adulthood. However, have improved drastically over the past few decades, so nearly all children with heart defects survive into adulthood. However, if you have congenital heart disease you might need care throughout your life.
Doctors have not been able to exactly know why some children are born with Congenital Heart Disease. However, they have accounted for several risk factors which are responsible for contributing to the high probability of catching a Congenital Heart Disease. They are:
On an often basis, a congenital heart defect is diagnosed during a pregnancy ultrasound. If the doctor observes anything abnormal with the fetus heartbeat, he would proceed with further tests to investigate the issue. These tests may include an echocardiogram, a chest X-ray, or an MRI scan. On the other hand, some babies are detected with a Congenital Heart Disease after they are born. The symptoms associated with the following:
There are a lot of types of Congenital Heart Defects, which are categorized according to the area they are present in. The most common types of Congenital Heart Defects:
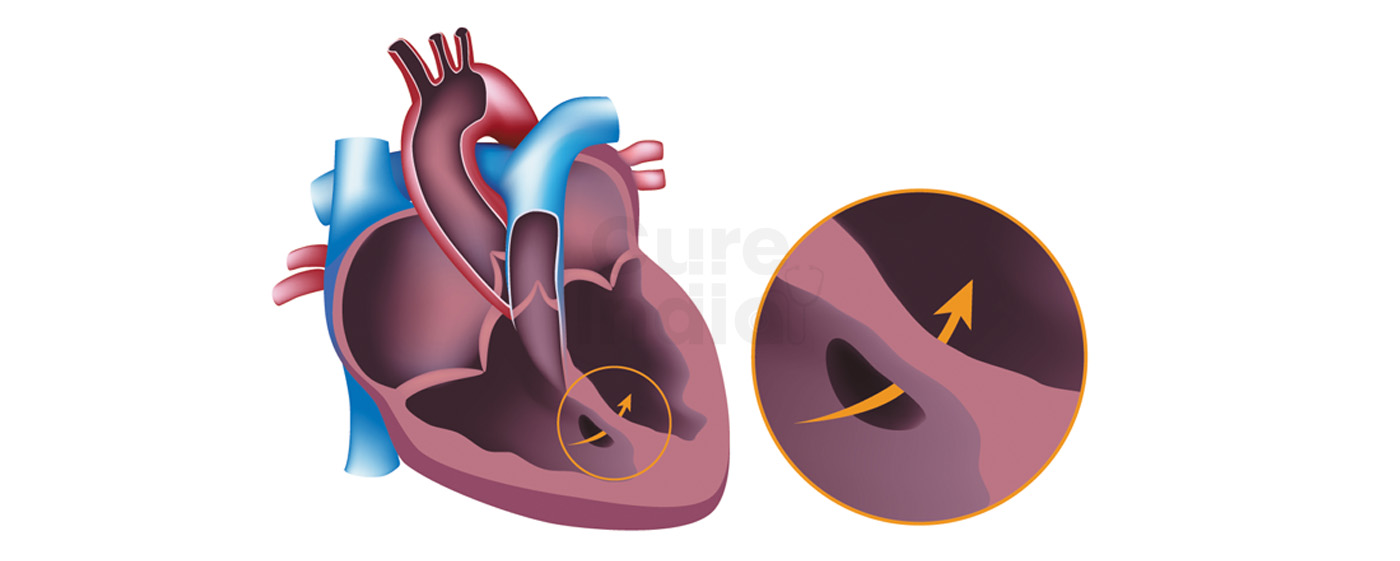
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a common type of Congenital Heart Disease which present due to a hole in the wall of the heart which is present between the two upper chambers of the heart. Children are born with this defect.
If small, many atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood but larger atrial septal defects are a threat which can cause severe complications to the heart and lungs.
Atrial septal defect (ASD) signs and symptoms may include:
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is also a hole in the heart, and is as common during the childbirth as an atrial septal defect (ASD). The hole is present in the wall which separates the lower chambers of the hearts enabling the blood flow from the left to the right side of the heart.
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) symptoms in a baby may include:
Cardiac patients from Arabic nations like UAE, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Iraq visit India seeking the best cardiac treatments. In India, cardiac hospitals are constantly upgrading to provide the latest and most modern diagnostic and treatment services. Indian cardiac hospitals are providing robot-assisted ASD and VSD repair procedures that are performed with a beating-heart approach. As compared to other countries, the cost of ASD/VSD Repair treatment in India is much less. Mentioned below is the cost of ASD/VSD Repair in India
| Treatment | Cost |
|---|---|
| ASD/VSD Repair Treatment in India | 6000-7000 USD |
The type of congenital heart defect treatment is highly subject to the type and how complicated the defect is. For a serious case of Congenital Heart Disease, one or more of the following congenital heart defect treatment options can be adopted:
The doctor may prescribe a set of medicines so that heart works more in a normal manner. Many medications are used to prevent the formation of blood clots and to prevent heart palpitations.
In more complicated cases of a congenital heart defect, the doctor may recommend for the installation of devices like a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs). A pacemaker installation will help regulate the heartbeat while an ICD corrects severely irregular heartbeats.
Catheterization/ ASD and VSD Device Closure is a technique which enables the cardiologists to fix and cure several congenital heart defects without making any incision in the chest or the heart. In treatments like these, the cardiologist inserts a thin tube into a vein present in the leg and guides it towards the heart. Once the correct positioning is achieved, the doctor employs small tools which he uses along the thing tube to operate the ASD and VSD.
When the catheter procedure fails to fix congenital heart defect, the cardiologist may go ahead to perform an ASD and VSD Surgical Closure which consists of an open-heart surgery which is used to seal holes in the heart (like the ASD and VSD), to repair heart valves, or widen the blood vessels which are narrowed and interfere with the blood flow.
A heart transplant is performed in very rare cases of congenital heart defect when there is no other treatment that is able to repair the defects. During this procedure, the defected heart is replaced with a healthy heart from a donor.
