

Clubfoot disease is a congenital disease where the child’s foot becomes inwards or downwards at the time of birth and remains in the same position for the rest of their life. The condition can range from being mild and flexible to severe and rigid. Clubfoot is a common congenital defect globally and people from African countries including Tanzania, Ghana, Ethiopia and Uganda visit India for cost-effective club foot surgery.
India offers the cheapest club foot surgery without compromising on the quality and reliability of the club foot treatment. Also, here you can get access to the premium-class medical infrastructure, globally acclaimed surgeons, advanced equipment support and highly-qualified and dedicated medical staff that ensure higher success rates and reduced chances of risk. So, if you are searching for a high quality yet affordable clubfoot surgery then choose India for your medical tourism.
Club foot is a congenital deformity of the lower foot of the fetus. The severity of club foot varies from one case to another depending on the type, environmental and genealogical factors. So, it would be wise to learn about the types and causes of club foot before opting for club foot surgery. Club foot disease can be categorised into three groups. Below we will discuss the types of the Clubfoot condition briefly:
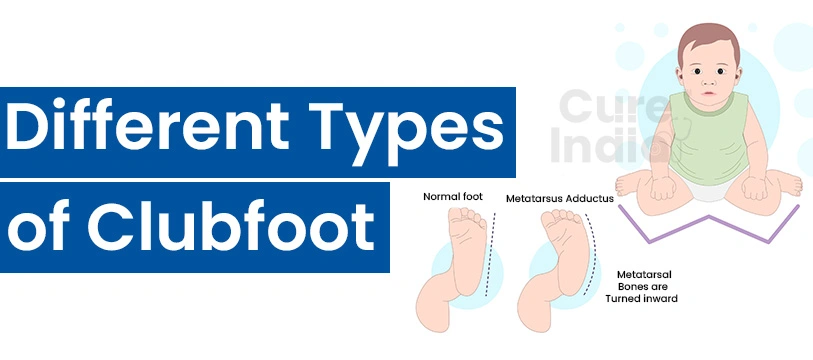
Idiopathic Clubfoot is also known as talipes equinovarus. It is one of the most common types of Clubfoot that are present at the time of birth. It is present in almost every one out of 1,000 newborn babies among which half of them only have one newborn clubfoot. There is no known cause of idiopathic clubfoot; however, baby boys are twice as likely to develop clubfoot than baby girls.
Neurologic clubfoot is relatively rarer than idiopathic clubfoot. It is caused due to an underlying neurological. For example, a baby born with spina bifida (A neural defect) can develop clubfoot later in childhood due to spinal cord compression or cerebral palsy.
Syndromic Clubfoot is mostly found with other underlying clinical conditions. These conditions are usually linked with the underlying syndrome. For example, a clubfoot can result from constriction band syndrome, dystrophic dwarfism, tibial hemimelia or arthrogryposis.
Clubfoot disease is a type of foot deformity that occurs at the time of birth. It ranges from mild and flexible to severe and rigid. Even though all clubfoot does not require a surgical intervention to correct the problem. In mild cases, medication, physiotherapy and self-stretching work well. So, if you are considering clubfoot surgery for adults or children, you must learn about the common clubfoot symptoms or indications that tell performing clubfoot surgery is essential:
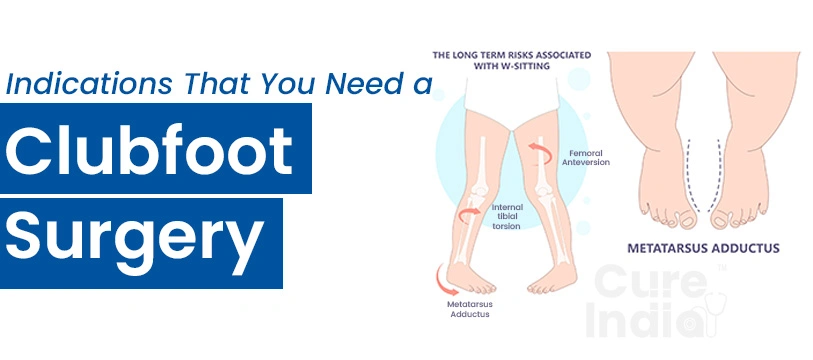
Clubfoot disease is a type of congenital deformity of the foot. It is more common in a male child than in a female child. Clubfoot surgery is mostly preserved for serious cases. A clubfoot surgery can be divided into different types depending on the type of clubfoot disease, age of the patient and severity of the case. Here are some common types of clubfoot surgeries popular globally:

Tenotomy is one of the most popular clubfoot correction methods for newborn babies and young adults according to experts. This surgical club foot treatment is only prescribed for newborns, and young children under 6-& years. This procedure involves making a small incision to reach the Achilles tendon and cutting/expanding it according to the need.
Osteotomy is another popular club foot treatment for both young and adults. In osteotomy, the surgeon removes certain parts of the bone that cause the arch and prevent the foot from reaching the right alignment.
Arthrodesis is another popular adult club foot surgery. When clubfoot is not treated in childhood arthrodesis or Fusion work best to treat the condition. In this condition two or more bones and fused. Here, the surgeon took bone from any other parts of the body to complete the procedure.
Sometimes pins, screws and casts are used as a part of clubfoot surgery and help to keep the foot in the correct position for a few days after surgery.
Clubfoot is a congenital condition where a baby’s foot is twisted out of shape or position. Early diagnosis and treatment often starting shortly after birth help in achieving normal foot function. India is home to a number of orthopedic surgeons and pediatric specialists who are highly experienced in treating clubfoot using methods like the Ponseti technique or surgical correction when necessary. Some of the best doctors for clubfoot treatment in India include:
Dr. Aashish Chaudhry is recognised as the best clubfoot correction doctor in India, with expertise in performing congenital foot deformities, limb lengthening, and pediatric orthopaedic surgeries. He specialises in performing surgical and non-surgical interventions for clubfoot treatment, providing children with corrected foot alignment, pain-free walking, and long-term functional improvements.

Dr. Sanjay Sarup is a top doctor for clubfoot correction surgery in India, specialising in providing treatments for complex congenital foot deformities, pediatric orthopaedic surgeries, and limb reconstruction. He uses state-of-the-art surgical techniques for clubfoot correction, focusing on long-lasting outcomes and minimal recurrence.

Dr. Nargesh Agrawal is an expert clubfoot treatment doctor in India, specialising in pediatric orthopaedics, congenital deformity correction, and minimally invasive clubfoot surgeries. He specialises in treating infants and children with congenital talipes equinovarus using modern techniques, like the Ponseti method and other surgical corrections.

Dr. Manoj Padman is a top-rated clubfoot treatment doctor in India, with extensive experience in surgical and non-surgical management of congenital foot deformities. He is specialised in treating infants and children with clubfoot, congenital talipes equinovarus, and other foot deformities.

Clubfoot surgery is also known as tenotomy (ten-AH-toe-me) which is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that helps to correct the condition of clubfoot. Clubfoot is a physical deformity that affects the normal formation of the foot and is present at the time of birth. In severe cases of clubfoot, a surgical procedure is necessary to correct the condition. And before you opt for clubfoot surgery for children or adults, you might like to learn about the procedure to make an informed decision:
*Note: In most cases, the child/adult is not unconscious as they will not give general anesthesia for the procedure. Instead, they use local anesthesia or numbing lotion to numb the feet for the surgery.
Clubfoot in infants is a common occurrence. Clubfoot disease is mostly common in male children than female children. However, not all club foot causes require a surgical intervention. The surgical procedure is preserved for only the most severe and complex cases where no other treatment works. So, if you are looking a surgery to correct club foot disease you might find alternative treatment methods helpful for non-severe and mild cases:

The Ponseti method to correct clubfoot is one of the most popular and effective non-surgical alternatives to straighten curved feet. The Ponseti method is used to correct clubfoot without surgical intervention. In this procedure surgeon uses multiple casting to treat the clubfoot.
Braces are also helpful non-surgical alternatives for infant clubfoot treatment. Braces help to keep feet straight.
Mild cases of clubfoot can also be corrected with physiotherapy and guided stretching, helpful for mild clubfoot cases.
After a club foot surgery, a surgeon will put your child's leg in a toe-to-thigh cast for at least 7-8 weeks. The cast is changed every week as tendons heal in the corrected position. The club foot specialist then removes the cast and recommends using a brace. This brace also needs to be changed in regular intervals for at 4 weeks for complete healing. Physical therapy is also advised in club foot surgery cases. Consult with your child's surgeon to know more about recovery time and post-operative care.
The cost of club foot surgery in India depends on the hospital charges, location, surgeon’s fee and other medical expenses. Generally, you can expect the cost of club foot surgery to range from USD300 to USD500. Talk with your healthcare provider for an accurate cost estimation for the procedure. Always choose a healthcare provider who can offer transparent price breakdowns and payment options.
| Treatment Name | Cost in India | Stay in India |
|---|---|---|
| Clubfoot Surgery in India | $3,800 - $4,500 | 4 - 5 Weeks |
Whether your existing insurance plan will cover the cost of club foot surgery or not depends on the type of policy and its terms and conditions. Some policies can cover the charges of the procedure while others may offer coverage of other related expenses. Consult with your insurance provider and healthcare provider to more about the insurance coverage for club foot surgery.


Globally Trusted Brands
Inquire Now
Knee, Hip and Shoulder Replacements
Share Your Reports
Computer Navigated and Keyhole Knee Surgeries
Recover Fast