

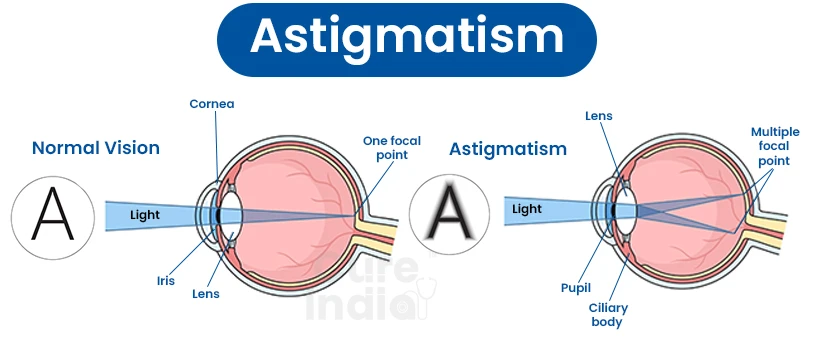
A frequent eyesight issue called Astigmatism is brought on by a refractive error. The error may be present either in the cornea's shape or in the lens. Individual differences may exist in symptoms, such as blurred vision and night blindness.
The cornea, or front surface of the eye, has an uneven curvature when Astigmatism is present. This may alter how light refracts or travels through your retina, leading to distorted, hazy, or blurry vision. The optimal treatment method for this condition is surgery, but secondary methods can include wearing glasses and contact lenses. If surgery is your preferred option, Indian is one of the best countries for getting eye surgeries. You will find that the eye surgery for astigmatism in India is not only affordable but very high-quality and performed by certified ophthalmologists.
Another two conditions affecting how light reaches your retina are farsightedness and nearsightedness. Hyperopia is the term used to describe farsightedness. The time for nearsightedness is myopia.
The two main kinds of Astigmatism are 1) lenticular and 2) corneal—a distortion or flaw in the cornea results in corneal Astigmatism. When the lens is distorted, lenticular Astigmatism occurs.
The terms regular and irregular are also occasionally used to characterize astigmatisms. The result of partial curvature of the eye is a regular astigmatism. Thus, it may resemble a football rather than being round like a basketball. This frequently results in distorted, fuzzy eyesight.
Astigmatism's etiology is unknown, although heredity plays a significant role. Although it may arise later in life, it is frequently present from birth. It could also happen following eye surgery for Astigmatism or as a result of an eye injury. When nearsightedness or farsightedness coexist, Astigmatism frequently results.
However, Astigmatism can occasionally be brought on by keratoconus, an uncommon ailment. The transparent tissue on the cornea thins and protrudes due to this eye condition. This causes sensitivity to bright lights and foggy or fuzzy vision. Although the exact cause of keratoconus is uncertain, it is thought to run in families.
Remember, reading in low or dim lighting can produce eyestrain. However, it does not impair vision or lead to Astigmatism. Existing Astigmatism may cause increased blurriness when reading in low light.
Both adults and children can develop Astigmatism. If you have any of the following, you may be more likely to acquire Astigmatism:
An optometrist treats Astigmatism through an eye exam. During a vision test, your eye doctor will scan your eyeball. They measure every square inch of its surface in three dimensions.

Your eye doctor can identify the high and low regions of the cornea that cause Astigmatism. This is done using sections of the eye called meridians. A unit of measurement or diopter is used to estimate each meridian's refraction amount.
Optometrists and ophthalmologists may perform various tests during your eye exam. These tests help determine whether you are in need of eye surgery for astigmatism in India:
Your doctor will ask you to read letters during a visual acuity evaluation exam. This is done from a chart at a specified distance. This helps gauge your visual acuity.
An optical refractor is a device used in refraction tests. The device contains several different strengths of corrective glass lenses. When using the optical refractor, your doctor will ask you to stare through lenses of varying strengths while reading a chart. Eventually, they'll locate a lens that properly corrects your eyesight.
Your doctor can determine the curvature of your cornea using keratometry. They will use a keratometer to examine your eye to accomplish this.
Astigmatism is common in newborns but usually goes away in the first year. Astigmatism rarely manifests in children by the time they are 5 to 9 years old.
Some kids never grow out of their Astigmatism. Untreated Astigmatism can hinder development and learning.
It is crucial to arrange regular eye exams for youngsters. This helps identify untreated refractive problems, such as Astigmatism.
The cornea and lens in front of the eye should be spherical. This aids in finely focusing light beams onto the retina to improve vision.
Light rays do not correctly refract or bend as they enter the front of the eye when they have Astigmatism. Vision becomes hazy at close range and distance. Light rays either miss the retina entirely or pass behind it.
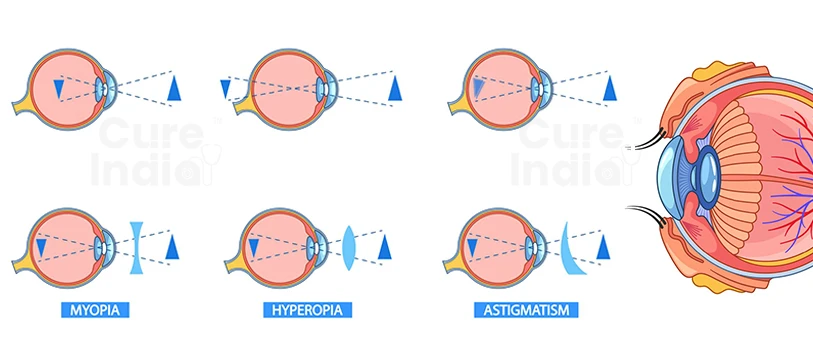
Astigmatism can coexist with other refractive defects in certain people, including:
Your doctor's advice determines the best course of action for you. Factors like your prescription, corneal thickness, eye health, and daily activities impact the decision.
Astigmatism glasses are a common, easy alternative with many possibilities. They can achieve 20/20 vision by correcting mild to moderate regular Astigmatism. The eyes' uneven curvature is considered when crafting the lenses.
With many variations, contact lenses for Astigmatism are another well-liked option. Regular Astigmatism with mild or low levels can occasionally be corrected with regular soft contacts.
Moderate to high regular Astigmatism often requires rigid or toric gas permeable (RGP) contacts. Customized RGP and scleral lenses are good options for people with irregular Astigmatism.

For milder forms of Astigmatism, orthokeratology is an option. It's also known as corneal refractive therapy or Ortho-k and can be used as a temporary correction.
This procedure involves wearing specially made hard contacts overnight. They are designed to restructure the cornea slightly and are removed upon waking. The effects generally wear off within a day or two if the connections are worn infrequently.
The only method to permanently treat Astigmatism is surgery. Surgery is the best option, depending on various criteria. These include your age, corneal thickness, type and degree of Astigmatism, and other eye diseases.
There are several laser eye surgery for astigmatism in India you may opt for. These techniques aim to alter the shape of the cornea. Among them are:
Using eye exercises to treat refractive defects has been around for a while. However, there needs to be proof that these methods, including those for Astigmatism, are effective.
The cornea or lens form causes Astigmatism, which results in distorted and fuzzy vision. The rectus muscles, which move the eyes around, are worked during eye exercises. Strengthening these muscles can help with strabismus (crossed eyes) and amblyopia (lazy eye). It cannot alter the structure of the cornea or lens.
Experience and expertise are the first criteria when choosing an eye surgeon. An experienced eye surgeon helps you provide the expected results. CureIndia has the best eye surgeons for performing eye surgery for astigmatism in India the way you want.
Dr. Suraj Munjal is the best eye specialist in Delhi NCR. He has done many refractive surgery, astigmatism surgery, and cornea transplants with a wide variety of complicated cases. He also has expertise in all types of LASIK eye surgeries.

Dr. Suwarn Chetan is an ophthalmologist specializing in Occuloplasty and LASIK surgeries to cure astigmatism. He is one of the top eye specialists in India for cataract eye surgery, refractive eye surgery, and pediatric ophthalmology.

Dr. Neeraj Sanduja is the most experienced eye specialist in Delhi NCR. His expertise includes LASIK surgeries, diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, ocular trauma, retinopathy of prematurity, and macular holes.

Dr. Sumit Gupta is a specialist eye doctor in Gurgaon, India. He has proficiency in Cataract and vitreo retinopathy. He is also an expert in LASIK eye surgery with a high success rate.

Astigmatism is a common refractive error that causes blurred or distorted vision due to an irregularly shaped cornea or lens. Fortunately, several effective treatment options are available in India at a fraction of the cost compared to many Western countries.
The overall cost of astigmatism treatment in India depends on multiple factors such as the type of correction method chosen, the hospital, the surgeon’s experience, diagnostic procedures, and post-treatment care. Surgical correction, like LASIK or other laser-based procedures, tends to be more expensive than non-surgical solutions but offers long-term results. Here is the cost of different astigmatism treatments available in India, along with recommended stay in the country:
| Treatment Name | Cost in India | Stay in India |
|---|---|---|
| LASIK Eye Surgery for Astigmatism in India | $1,000 (both eyes) | 5-7 Days |
| Robotic LASIK Eye Surgery for Astigmatism in India | $1,500 (both eyes) | 5-7 Days |
| SMILE LASIK Eye Surgery for Astigmatism in India | $2,000 (both eyes) | 5-7 Days |
| ICL Eye Surgery for Astigmatism in India | $3,500 (both eyes) | 5-7 Days |


Get the Eye color you've always dreamed of
Connect Today
Opt for successful eye color change surgery
Plan Surgery
Remove glasses with SMILE LASIK
Get Cost