

A cervix is a part of a female reproductive system and is present between the uterus and the vagina. It is the narrow, lower end of a uterus that allows the menstrual blood to pass from the uterus to the vagina and it widens during labor (childbirth) to deliver the baby. The cervix is made up of two parts, the outer part is known as the ectocervix, and the inner part is known as the endocervix. Cervical cancer occurs when the cells of the cervix start to grow uncontrollably forming a mass/group of cells known as a tumor. This tumor can either be a benign tumor (stays at its particular location) or it may be malignant (spreads to the other parts of the body). The main causes of vaginal cancer is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). It is a virus that spreads via sexual activities. When the cervical cells are infected, they start to grow abnormally in their precancerous stage, they are known as atypical cells. These cells undergo slow changes and develop into the cancer cells. This phase where the abnormal cells grow at its precancerous stage on the surface of the cervix is known as cervical dysplasia. As these cells continue to make changes, they develop into cancer.
Cervical cancer is the 4th most common type of cancer in women. About 604,000 new cases were diagnosed in the year 2020 out of which about 342,000 women died. The low and middle-income countries have the highest cases of cervical cancer with high incident rates and mortality rates due to a lack of population-wide HPV vaccination, regular screening of the cervix, and treatment services. It is reported that cervix cancer is the leading cause of death in women due to cancer in Sub-Saharan Africa. The women who have HIV are six times more susceptible to developing cervical cancer than women who do not have HIV. Prevention, early diagnosis, and early treatment are very effective in reducing cervix cancer rates.
Due to the effective HPV vaccination, the cases of cervix cancer have reduced dramatically in high-income countries. However, the countries of Sub-Saharan Africa are facing many challenges in controlling cervix cancer rates due to a lack of proper screening programs for cervical cancer, financial constraints, logistic constraints, and a lack of preventative measures. According to the reports, the incidence rate of cervix cancer will rise causing about 443,000 deaths annually by 2030 with 90% of mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa. Due to insufficient preventative, diagnostic, and treatment protocols in their countries, many people from Cameroon, Rwanda, Kenya, and Uganda travel to India for getting the cure for cervical cancer by the best oncologists in the country. Choosing India for medical treatments is much more affordable and profitable to people visiting from African countries as the cost of cervical cancer treatment in India is very low when compared to western countries.

On the basis of from which cell the cancer has started, and how they look under the microscope, there are different types of cervical cancer. They are listed below.
Most of the cervical cancers are of this type. This type of cancer starts from the cells where the endocervix and ectocervix meet. These cells are known as squamous cells which are flat and cover the ectocervix. The squamous cell carcinoma accounts for 90% of cervix cancer cases.
The cervix contains glandular cells that secrete the mucus. These cells are present in the endocervix. Adenocarcinoma is a little less common than squamous cell carcinoma, but it has started to become common in recent years. It accounts for about 20% of cervix cancer cases.
It is a rare type of cervical cancer which is a mixture of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. This type of cervical cancer is also known as Mixed carcinoma. It forms the tumor that contains both the squamous cells and the glandular cells. It accounts for only 3 to 10% of cervix cancer cases.
Some other very rare cervix cancer types are small cell cancer, lymphoma, sarcoma, glassy cell carcinoma, neuroendocrine carcinoma, etc. These are very rare and different from the above mentioned common types of cervical cancer.
Besides the types of cervical cancer, there are three grades of cervical cancer. The grades show us what type of cervical cancer you might have and what the cells look like under the microscope. Grade 1 is a low grade and the cancer cells look like normal cells. Grade 2 cancer cells look a little bit like normal cells with slight changes, and Grade 3 which is high-grade cancer cells look very different from the normal cells of the cervix.
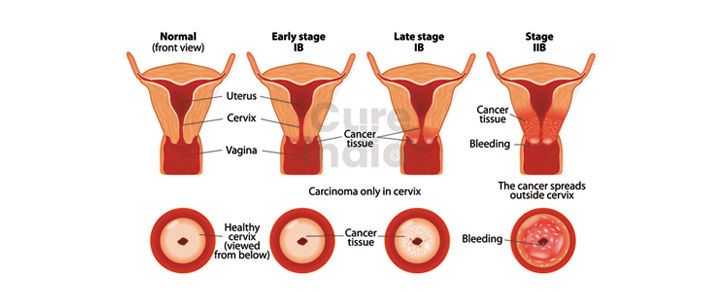
The cervix cancer is divided into different stages to understand the severity of the cancer. The stage of a cancer tells about the size of the cancer/tumor and whether it has spread to other body parts or not. The different stages of cervix cancer are listed below.
■ Stage 1 cervical cancer: The stage 1 cancer is an early stage of cervix cancer. It means that the cancer cells are present in the cervix only and it has not spread. It is further divided into stages such as stage 1A (1A1, 1A2), and stage 1B (1B1,1B2,1B3).
■ Stage 2 cervical cancer: If you have stage 2 cancer, then the cancer has spread from the cervix to the surrounding tissues like the vaginal tissues. It is also divided further into stages such as stage 2A (2A1, 2A2) and stage 2B.
■ Stage 3 cervical cancer: In stage 3 cancer, the cancer spreads from the cervix to the surrounding organs like the vagina, pelvic wall, lymph nodes, etc. It causes swelling in the kidney (hydronephrosis). It is further divided into subtypes like stage 3A, stage 3B, and stage 3C (3C1, 3C2).
■ Stage 4 cervical cancer: If you have stage 4 cervix cancer that means the cancer has spread from the cervix to the rectum and the urinary bladder, or it can also spread to other organs of the body. This stage is also divided into stage 4A and stage 4B.
A precancerous stage of cervical cancer does not show any symptoms. The symptoms start to appear when the precancerous cells convert into cancerous cells, and it reaches the early stage of cervical cancer. In the start, you will only have a few symptoms and then the symptoms can be more severe when the cervical cancer progresses to an advanced stage.
The early-stage cervix cancer symptoms include:
If the early diagnosis and treatment for the cervical cancer in women have not proceeded, the early-stage cervix cancer can transition to an advanced-stage cervix cancer and it can start spreading to the other parts of the body and you will experience severe symptoms.
The advanced-stage cervical cancer symptoms include:
The most common cause of vaginal cancer is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Women are most likely to get the HPV infection after becoming sexually active as the HPV virus Is spread via any form of sexual activity. There are about 100 different types of HPV virus but not all are linked to cause cancer.
.jpg)
HPV16 and HPV18 are the two strains/types of the HPV virus that are linked with causing cancer. These two strains are responsible for 70% of cervix cancer cases worldwide. Becoming sexually active at a very young age, having multiple sexual partners, unprotected intercourse, having AIDS, having a weakened immune system, not getting the HPV vaccination, etc. increases your risk of contracting an HPV infection.
There are many other risk factors that increase your susceptibility to HPV infection or cervical cancer. They include poor immune system, smoking, herpes infection, old age, some socioeconomic factors, exposure to DES, oral contraceptives, obesity, etc. If your immune system is weak, you are more sensitive to cervical cancer.
You may have immunosuppressive medications for certain medical procedures like organ transplantation or due to the presence of another disease in the body such as HIV. Having genital herpes also increases the chance of getting cervix cancer. Cervix cancer is also seen in people who don’t have access to proper cervical cancer screening and vaccinations and most of them are from low-middle income countries. The people whose mothers were given a diethylstilbestrol drug to prevent a miscarriage during a pregnancy also have an increased chance of developing cervical cancer.
There are so many diagnostic tools to detect the presence of cervical cancer in women. The patient does not need to go through all of the diagnostic tests. Your doctor will determine what diagnostic tests you might need based on the symptoms you are having. The common tests for the diagnosis of cervical cancer are as follows:
■ Gynecologic exam: It is also known as the Bimanual Pelvic Exam and Sterile Speculum Exam. In this test, your doctor will check any abnormalities present in the vagina, cervix, uterus, ovaries, and nearby tissues and organs. Your doctor will use a speculum which is a medical tool to keep the vagina open during the physical exam.
■ Pap test: During a pap test, your doctor will brush and scrape the cells from your cervix to collect the sample and then it is sent to the laboratory to visualise the different looking cells. The cancer cells look different than the normal cells which can be detected under the microscope. It can also detect the precancerous cells.
■ HPV DNA test: This test is done to check the presence of the HPV infection. The cells are collected from your cervix and then sent to the laboratory to check the presence of 14 different types of HPV viruses which include HPV16 and HPV18.
In both of these tests, you will be told to lie on the table with the footrest and your doctor will open up your vagina with the medical tools to see the cervix. Then your doctor will collect the cells of the cervix by gently scraping it.
■ Colposcopy: A colposcope is an instrument that is similar to the microscope but it shows the more clear and magnified view of the cells and tissues of the internal organs of female reproductive tissue. For this test also, the tissue sample is first collected from the patient’s cervix and then it is sent to the lab for testing.
■ Biopsy: A biopsy is an important diagnostic test that requires a small tissue sample to be examined under the microscope. The biopsies are performed by the lab specialists known as pathologists. There are many types of biopsies used for the diagnosis of cervical cancer which include Endocervical Curettage (ECC), Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP), and Conization (also known as cone biopsy).
■ Imaging tests: The imaging tests are used to create images of the body and by doing so, the size and location of the cancer cells and tumors can be detected. There are many imaging tests that your doctor chooses from. The different imaging tests include an X-ray, CT Scan, MRI Scan, PET Scan, Ultrasound, etc.
■ Molecular test: This is a test that identifies the specific proteins, genes, and other unusual factors that are present in the tumor. These factors are different from the normal cells and hence we can differentiate the cancer cells and the normal cells. It is also known as a Biomarker test.
Besides these tests, if you have symptoms related to the rectum and urinary bladder problems, then the following tests will be helpful to determine if it is related to cervix cancer or is a completely different medical problem.
■ Cystoscopy: This procedure is used to visualize the internal part of the urinary bladder and the urethra. During this test, your doctor will insert a flexible, thin tube that has an attached light known as a cystoscope through the urethra. This method is used to check whether the cancer has spread to the urinary bladder.
■ Sigmoidoscopy: It is also known as proctoscopy. It is a procedure that is used to visualize the colon and the rectum. During this test, your doctor will insert a flexible, thin, lighted tube which is known as a sigmoidoscope through the rectum to check whether the cancer has spread to the rectum or the colon.

Cervical cancer surgery is the procedure to remove cancerous tissue from the uterus and cervix from a woman's body. CureIndia helps you choose the best cervical cancer doctor in India. The oncologists with CureIndia are highly experienced with specialised knowledge to perform cervical cancer treatment in India. Let us hear from some of the best cervical cancer doctors in India.






The cost of cervical cancer treatment in India can vary largely as different patients require different types of treatment and duration of the treatment. The total cost of the treatment depends on the stage of cervix cancer, the treatment approach selected, the selected hospital, the expertise of your oncologist, the location of the hospital, health insurance coverage, etc. However, on average, the cost of cervix cancer treatment in India can range from $2,000 to $6,000.
.jpg)
The cost of the same procedure in the USA ranges from $25,767 to $107,532 and in the UK it ranges from $13,500 to $14,070. The costs of different cervix cancer treatment in India are given below:
| Procedure | Cost in India |
|---|---|
| Chemotherapy for cervical cancer treatment in India (per session) | $2,000 - $6,000 |
| Radiation therapy | $1,500 - $6,000 |
| Immunotherapy | $1,500 - $5,000 |
| Surgery | $2,000 - $3,500 |
With the decreased cost of cervix cancer treatment, the diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for the treatment of cervix cancer are regularly updated in India. India has achieved the trust of international patients, especially people coming from African countries due to the enhanced medical awareness campaigns, constant upgrading of healthcare infrastructure, and the adoption of innovative and advanced medical technologies. The low cost of treatment makes it feasible for the patients visiting from Africa to receive the best treatment procedure.
There are various types of treatment options available in India for cervical cancer. Your oncologist may recommend the use of a single treatment procedure or a combination of treatments to cure the disease faster and more effectively. The selection of treatment depends on many factors like stage and type of cervix cancer, patient’s overall health, etc. The different treatment options for the cervical cancer in women are as follows:
Radiation therapy involves the use of high energy like X-rays to kill the cancer cells. There are two types of radiation therapy; Brachytherapy (BT), and External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT). The brachytherapy involves use of a medical device and placing it into the patient’s vagina and the uterus for a short period of time. This is either done periodically or continuously for a few days whereas EBRT involves the use of radiation outside the body and the X-rays are targeted to the area in the body where the cancer is present. This is done once a day for five days in a week up to 5 or 6 weeks.
.jpg)
Chemotherapy involves the use of complex medicines either orally or intravenously to stop the growth of the cancer cells and kill them. Sometimes these medicines are given in the muscles with the injections. In many cases, chemotherapy is used in combination with radiation therapy which is known as chemoradiation therapy.
This treatment method uses medicines (drugs) to attack and destroy the cancer cells. These drugs target the chemicals that are specific and only present in the cancer cells and block them so that the cancer cells die. This method is often combined with chemotherapy for the most effective results.
Our body’s immune system protects our body by destroying the cells and germs that are not good for the body. The cancerous cells hide from these immune cells so our immune system becomes incapable of finding and killing these cancer cells. What immunotherapy does is it helps our immune system to find the cancerous cells and kill them.
The surgery is a chosen treatment option for cancer that is localized and has not spread to the other parts of the body. Surgery is done to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding tissues. This helps in the prevention of the spread of the cancer in the other body parts. There are different types of surgery for cervical cancer. These are mentioned below:
■ Conization: This surgical procedure is used to remove the abnormal tissues. The conization is used to remove the microinvasive cancer which is the cancer that can only be visualized under the microscope.
■ Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP): This method uses a thin wire hook that passes the electric current to remove the cancer tissues.
■ Hysterectomy: It is a surgical procedure that is used to remove the uterus and the cervix. There are different types of hysterectomy procedures depending upon what tissues need to be removed along with the uterus. Radical hysterectomy involves the removal of the upper vagina, uterus, and the surrounding tissues along with the cervix whereas a simple hysterectomy involves the removal of the uterus and cervix only.
■ Bilateral Salpingo-oophorectomy: We can say that this procedure is a type of hysterectomy only. It involves the removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
■ Radical Trachelectomy: It is a surgical procedure that is used to remove the cervix but the uterus is kept as it is. This method is used when a woman wants to maintain her fertility, mostly young women.
■ Exenteration: This is a surgical procedure that is done when the cancer has spread from the uterus to the nearby organs. Along with the cervix, the vagina, uterus, lower colon portion, urinary bladder and the rectum are also removed.
You should start following the guidelines as soon as your treatment starts so that you will be used to it as the treatment progresses. The cancer of the cervix is a major disease that requires heavy treatment procedures. This puts a toll on the body and it is very important to maintain the fitness and health of the body so that it can respond to the treatments and medications in a better way.
Depending upon the type of treatment, your recovery time will be different. However, if the surgery is performed, you will need to stay at the hospital for about 3 to 4 days. It is recommended that you make some healthier lifestyle changes like healthy eating habits, regular exercise, proper sleeping schedule, etc. After a successful cervical cancer treatment in India, you will have follow-up tests every 3 to 4 months for the first two years. After that, you will have checkups every 6 months. The checkup is done to evaluate your overall health and to make sure that the cancer is not recurring.
Cervical cancer is one of the leading causes of death caused by cancer worldwide. With the preventative approaches, many high-income countries have reduced cervix cancer cases to a great extent. However, a lot of low-middle-income countries are still lagging behind due to insufficient healthcare infrastructure and expensive medical systems.
Due to this, many women do not receive the early diagnosis and treatment and as a result, most of the women diagnosed with cervix cancer in Africa have advanced stages of cancer. The cervix cancer can be managed and prevented from reaching the advanced stage if the right and proper diagnostic tests are done during the early stage or the precancerous stage of the cancer.
To avoid further complications in the body, many women from African countries are traveling to India for the proper treatment of cervical cancer. The low cost of the treatment is highly affordable to them and at such a low cost they receive world-class treatments.
